Match each class of drug with its descriptor – Matching each class of drug with its descriptor is a crucial aspect of pharmacology that enables healthcare professionals to accurately understand and prescribe medications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the different drug classifications, descriptors, and the process of matching them, providing a thorough understanding of this essential practice.
By understanding the mechanisms of action and characteristics of each drug class, we can effectively tailor treatment plans, minimize adverse effects, and optimize patient outcomes.
Drug Classification: Match Each Class Of Drug With Its Descriptor

Drugs can be classified into different categories based on their chemical structure, mechanism of action, and therapeutic use. Understanding drug classification is crucial for healthcare professionals to prescribe and administer medications safely and effectively.
Mechanisms of Action
Drugs exert their therapeutic effects by interacting with specific molecular targets in the body. The mechanism of action refers to the specific biochemical or physiological process that a drug modulates to produce its desired effect.
Examples of Drug Classes
- Analgesics: Relieve pain (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen, morphine)
- Antibiotics: Kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria (e.g., penicillin, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin)
- Antidepressants: Treat depression (e.g., fluoxetine, sertraline, venlafaxine)
- Antihypertensives: Lower blood pressure (e.g., captopril, losartan, amlodipine)
- Anticoagulants: Prevent blood clots (e.g., warfarin, heparin, aspirin)
Drug Descriptors
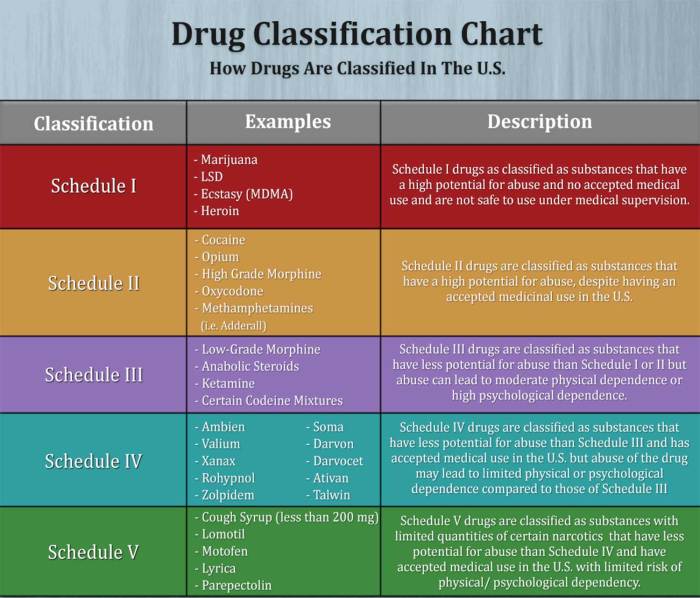
Drug descriptors are terms used to describe the characteristics, properties, and effects of drugs. They provide valuable information for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about drug selection and use.
Types of Drug Descriptors
- Pharmacodynamics: Describes the drug’s mechanism of action and its effects on the body
- Pharmacokinetics: Describes the drug’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
- Toxicity: Describes the potential adverse effects of the drug
- Dosage: Specifies the amount of drug to be administered and the frequency of administration
- Contraindications: Lists conditions or situations in which the drug should not be used
Matching Drugs to Descriptors
Matching drugs to appropriate descriptors is essential for safe and effective medication use. Healthcare professionals consider the drug’s mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, toxicity, dosage, and contraindications when selecting the most suitable drug for a particular patient and condition.
Matching Table
| Drug Class | Descriptors |
|---|---|
| Analgesics | Pharmacodynamics: Pain relief |
| Antibiotics | Pharmacodynamics: Antibacterial |
| Antidepressants | Pharmacodynamics: Antidepressant |
| Antihypertensives | Pharmacodynamics: Antihypertensive |
| Anticoagulants | Pharmacodynamics: Anticoagulant |
Exceptions and Overlaps, Match each class of drug with its descriptor
While most drugs can be classified into a single class, some drugs may have multiple mechanisms of action and thus fall into multiple classes. For example, aspirin is both an analgesic and an anti-inflammatory drug.
Additional Considerations
Importance of Matching
Matching drugs to descriptors is crucial for ensuring appropriate medication use. It helps healthcare professionals avoid adverse drug reactions, drug interactions, and other medication errors.
Challenges
Matching drugs to descriptors can be challenging due to the vast number of drugs available, the complexity of drug mechanisms, and individual patient variability. Healthcare professionals must stay up-to-date on the latest drug information and consider the patient’s unique circumstances.
Overcoming Challenges
- Regularly consult reputable drug databases and resources
- Stay informed about new drug approvals and updates
- Consider the patient’s medical history, allergies, and other medications
- Collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as pharmacists and nurses
Questions and Answers
What is the importance of matching drugs to descriptors?
Matching drugs to descriptors is crucial for accurate prescribing, understanding drug mechanisms, and ensuring patient safety.
What are some challenges in matching drugs to descriptors?
Challenges include overlapping drug effects, multiple descriptors for a single drug, and the need for individualized patient assessment.
How can we overcome these challenges?
Strategies include using reference materials, consulting with experts, and staying up-to-date with the latest drug information.