The human respiratory system worksheet answers – Unveiling the intricacies of the human respiratory system, this worksheet delves into the mechanisms, structures, and functions that govern our very breath. Prepare to embark on a journey of discovery as we explore the complexities of respiration, unraveling the mysteries that lie within our lungs.
Within this comprehensive guide, we will dissect the anatomy of the respiratory system, tracing the path of air as it flows through the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi, ultimately reaching the delicate alveoli within our lungs. We will uncover the vital role of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles in facilitating inhalation and exhalation, and delve into the intricate mechanisms of gas exchange that sustain our very existence.
Overview of the Human Respiratory System
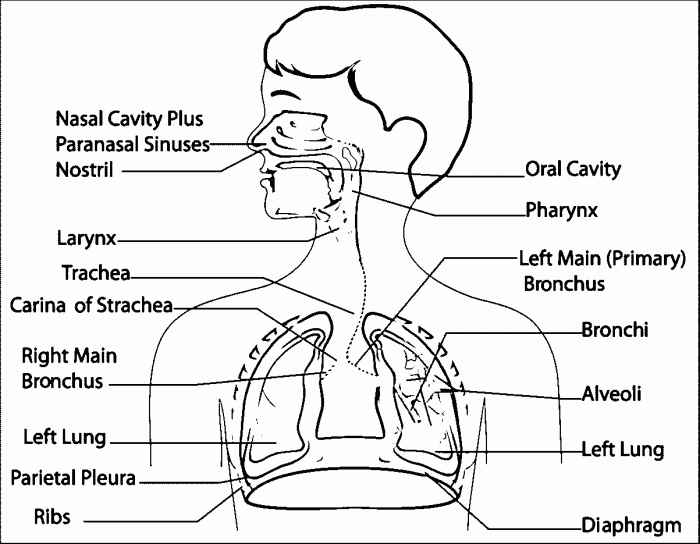
The human respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It consists of a series of organs and structures that work together to facilitate the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide.
The primary organs of the respiratory system include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. The nose and pharynx are involved in the initial filtering and warming of air before it enters the larynx, which contains the vocal cords.
The trachea is a tube that carries air to the bronchi, which branch into smaller tubes called bronchioles. The bronchioles lead to the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place.
Gas exchange occurs through the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the thin walls of the alveoli and the capillaries that surround them. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli.
This process ensures that the body receives the oxygen it needs while eliminating waste products like carbon dioxide.
Anatomy of the Respiratory System
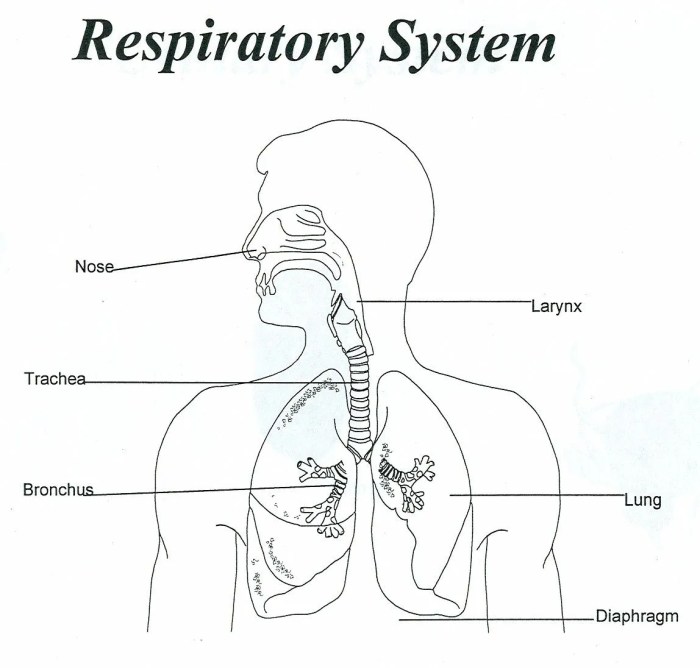
The human respiratory system is a complex network of organs and structures that work together to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. The main components of the respiratory system include:
- Nasal Cavity:The nasal cavity is the initial point of entry for air into the respiratory system. It is lined with mucous membranes that help filter and warm the air.
- Pharynx:The pharynx, also known as the throat, is a muscular tube that connects the nasal cavity to the larynx.
- Larynx:The larynx, commonly called the voice box, contains the vocal cords and is responsible for producing sound.
- Trachea:The trachea is a tube-like structure that carries air from the larynx to the bronchi.
- Bronchi:The bronchi are the two main branches of the trachea that enter the lungs.
- Bronchioles:The bronchioles are smaller branches of the bronchi that lead to the alveoli.
- Alveoli:The alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place.
- Lungs:The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system and are responsible for gas exchange.
Physiology of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system functions through the coordinated actions of various muscles and structures. The process of breathing involves two main phases: inhalation and exhalation.
Inhalation:During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and the intercostal muscles expand the chest cavity. This creates a negative pressure that draws air into the lungs through the nose and mouth. The air then travels through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles to reach the alveoli.
Exhalation:During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and the intercostal muscles contract, reducing the volume of the chest cavity. This creates a positive pressure that forces air out of the lungs through the same pathway it entered.
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli. The oxygen-rich blood is then transported to the heart and pumped throughout the body, while the carbon dioxide-rich blood is transported back to the lungs to be exhaled.
Common Respiratory Conditions
The respiratory system is susceptible to a variety of conditions that can affect its function and overall health. Some of the most common respiratory conditions include:
- Asthma:Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways that causes wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
- Bronchitis:Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi, which can be caused by infection, allergies, or irritants. It leads to coughing, mucus production, and chest discomfort.
- Pneumonia:Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation and fluid buildup in the alveoli. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and can lead to fever, chills, cough, and difficulty breathing.
Maintaining Respiratory Health
Maintaining good respiratory health is essential for overall well-being. Here are some tips for keeping your respiratory system healthy:
- Avoid Smoking:Smoking is one of the leading causes of respiratory problems. Quitting smoking can significantly improve lung function and reduce the risk of respiratory diseases.
- Exercise Regularly:Regular exercise helps strengthen the respiratory muscles and improve overall lung capacity.
- Get Vaccinated:Vaccinations against respiratory infections, such as the flu and pneumonia, can help protect your respiratory system from these diseases.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet:A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients for respiratory health.
- Practice Good Hygiene:Wash your hands frequently, cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoid contact with people who are sick to prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
FAQ Insights: The Human Respiratory System Worksheet Answers
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
The primary function of the respiratory system is to facilitate gas exchange between the body and the external environment, enabling the uptake of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide.
What are the key structures involved in respiration?
The key structures involved in respiration include the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
How does gas exchange occur in the lungs?
Gas exchange in the lungs occurs through the process of diffusion, where oxygen from the alveoli moves into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide moves from the bloodstream into the alveoli.