Embarking on a journey into the realm of worksheet organization of the periodic table, this comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of this essential tool for understanding the fundamental principles of chemistry. Through a captivating narrative, we delve into the systematic arrangement of elements, exploring their properties and applications.
Worksheet organization of the periodic table provides a structured framework for students to grasp the organization of elements based on atomic number, atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. This guide equips educators with worksheets and activities that reinforce understanding of group and period properties, fostering a deeper comprehension of the periodic table.
Understanding the Periodic Table
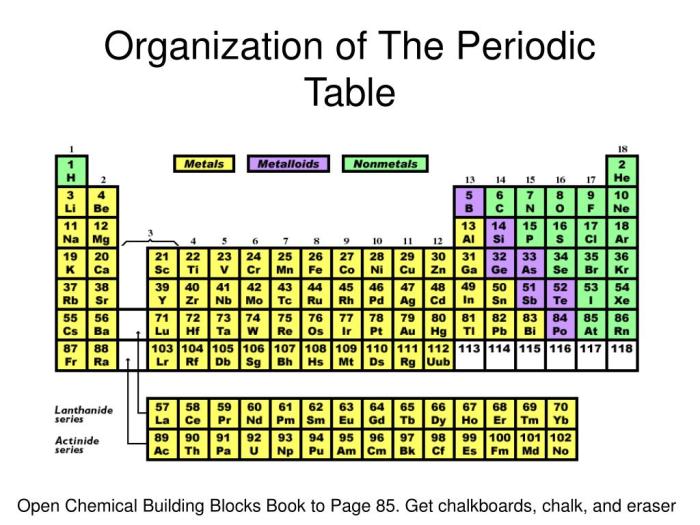
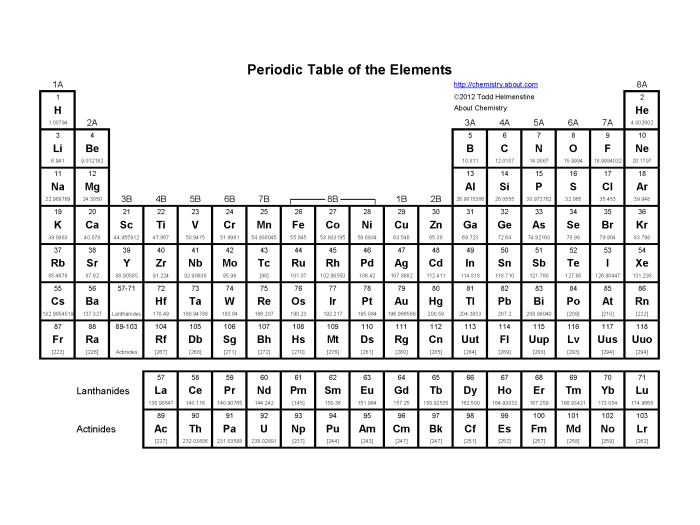
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It is a powerful tool for understanding the chemical behavior of elements and predicting the properties of new elements that have not yet been discovered.
The periodic table was first developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weight, and he grouped elements with similar chemical properties together. The periodic table has since been expanded and refined, and it now includes 118 elements.
Organization of Elements, Worksheet organization of the periodic table
The periodic table is organized into 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. The groups are numbered 1-18 from left to right, and the periods are numbered 1-7 from top to bottom.
The elements in each group have similar chemical properties. For example, the elements in Group 1 are all highly reactive metals, and the elements in Group 18 are all noble gases.
The elements in each period have the same number of electron shells. For example, the elements in Period 2 all have two electron shells.
Trends in Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy, and Electronegativity
There are several trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity across the periodic table.
- Atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period.
- Atomic radius increases from top to bottom down a group.
- Ionization energy increases from left to right across a period.
- Ionization energy decreases from top to bottom down a group.
- Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period.
- Electronegativity decreases from top to bottom down a group.
These trends can be explained by the changes in the number of electrons and the distance of the electrons from the nucleus.
Common Queries: Worksheet Organization Of The Periodic Table
What is the purpose of worksheet organization of the periodic table?
Worksheet organization of the periodic table provides a structured framework for students to learn about the organization of elements, their properties, and their applications.
How can I use worksheets to teach the periodic table?
Worksheets can be used to guide students through the organization of the periodic table, reinforce understanding of group and period properties, and explore real-world applications of the periodic table.
What are the benefits of using worksheets for periodic table instruction?
Worksheets provide a hands-on, interactive way for students to learn about the periodic table, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills.