Which of the following is an involuntary alienation of property – Involuntary alienation of property, a legal concept that often arises in real estate transactions, presents a compelling topic for exploration. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of involuntary alienation, examining its legal definition, various types, common causes, and potential consequences.
By unraveling the complexities surrounding this subject, we aim to provide a clear understanding of involuntary alienation and empower property owners with the knowledge to safeguard their rights.
Involuntary alienation encompasses situations where an individual’s ownership of property is involuntarily transferred to another party without their consent. This can occur through legal proceedings, government actions, or other circumstances beyond the owner’s control.
Involuntary Alienation of Property

Involuntary alienation of property is the transfer of ownership of property from one person to another without the consent of the owner. This can occur for a variety of reasons, including eminent domain, foreclosure, and tax sales.
Types of Involuntary Alienation
There are several different types of involuntary alienation, including:
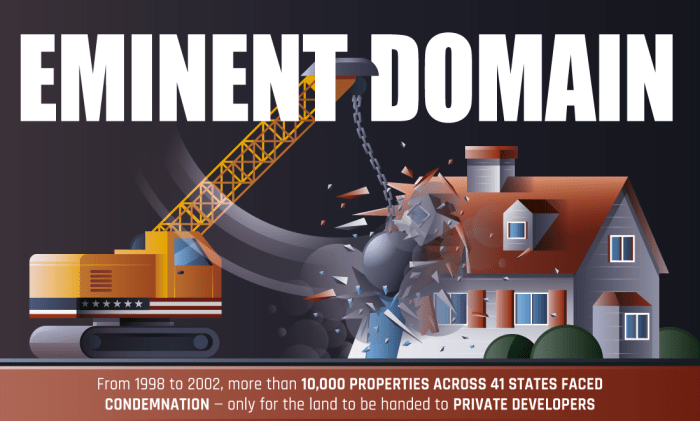
- Eminent domain:The government’s right to take private property for public use.
- Foreclosure:The sale of property to satisfy a debt.
- Tax sales:The sale of property to satisfy unpaid taxes.
- Partition:The division and sale of property owned by multiple people.
Causes of Involuntary Alienation
There are a number of common causes of involuntary alienation, including:
- Government action:The government may take property through eminent domain for a variety of purposes, such as building roads, schools, or hospitals.
- Mortgage default:If a homeowner fails to make mortgage payments, the lender may foreclose on the property and sell it to satisfy the debt.
- Unpaid taxes:If a property owner fails to pay property taxes, the government may sell the property to satisfy the debt.
- Partition:If property is owned by multiple people, one or more of the owners may file a partition action to have the property divided and sold.
Consequences of Involuntary Alienation, Which of the following is an involuntary alienation of property
Involuntary alienation can have a number of negative consequences for property owners, including:
- Financial loss:Property owners may lose the value of their property, as well as any equity they have built up.
- Emotional distress:Involuntary alienation can be a traumatic experience for property owners, who may feel like they are being forced to give up their homes or businesses.
- Loss of control:Property owners may lose control over their property, which can make it difficult to plan for the future.
Legal Remedies for Involuntary Alienation
There are a number of legal remedies available to property owners who have experienced involuntary alienation, including:
- Filing a lawsuit:Property owners may be able to file a lawsuit to challenge the involuntary alienation of their property.
- Seeking compensation:Property owners may be able to seek compensation for the loss of their property.
- Negotiating with the government:Property owners may be able to negotiate with the government to receive compensation for their property or to have the taking of their property delayed.
Question Bank: Which Of The Following Is An Involuntary Alienation Of Property
What constitutes involuntary alienation of property?
Involuntary alienation occurs when an individual’s ownership of property is transferred to another party without their consent, often through legal proceedings, government actions, or other circumstances beyond their control.
What are the different types of involuntary alienation?
Involuntary alienation can take various forms, including eminent domain, foreclosure, tax sales, and partition actions.
What are the common causes of involuntary alienation?
Involuntary alienation can result from factors such as government takings, mortgage defaults, unpaid property taxes, and court orders.
What are the legal remedies available to property owners who have experienced involuntary alienation?
Property owners may have legal remedies available to them, such as filing an inverse condemnation lawsuit, seeking compensation for damages, or challenging the validity of the involuntary alienation.