Antibiotic resistance brain pop video – Embark on a journey to understand the critical issue of antibiotic resistance through the captivating “Brain Pop” video. This educational resource provides a comprehensive overview of the causes, consequences, and strategies to combat this growing threat to public health.
Antibiotic resistance has emerged as a major concern in healthcare, with bacteria developing mechanisms to evade the effects of once-effective antibiotics. This video delves into the complexities of antibiotic resistance, highlighting its impact on human health and the urgent need for responsible antibiotic use and infection control measures.
Introduction

Antibiotic resistance is a significant global health concern. It occurs when bacteria develop the ability to resist the effects of antibiotics, making it difficult or impossible to treat bacterial infections. This phenomenon poses a major threat to public health, as it can lead to prolonged illnesses, treatment failures, and even death.
The “Brain Pop” video on antibiotic resistance provides an accessible and informative overview of this complex topic. It explains the concept of antibiotic resistance, its causes, and its potential consequences. The video also highlights the importance of responsible antibiotic use and infection control practices in combating this growing problem.
Causes of Antibiotic Resistance
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics
- Incomplete or improper antibiotic treatment
- Agricultural use of antibiotics
- Horizontal gene transfer among bacteria
Consequences of Antibiotic Resistance
- Prolonged and more severe infections
- Treatment failures
- Increased healthcare costs
- Limited treatment options
- Death
Causes of Antibiotic Resistance
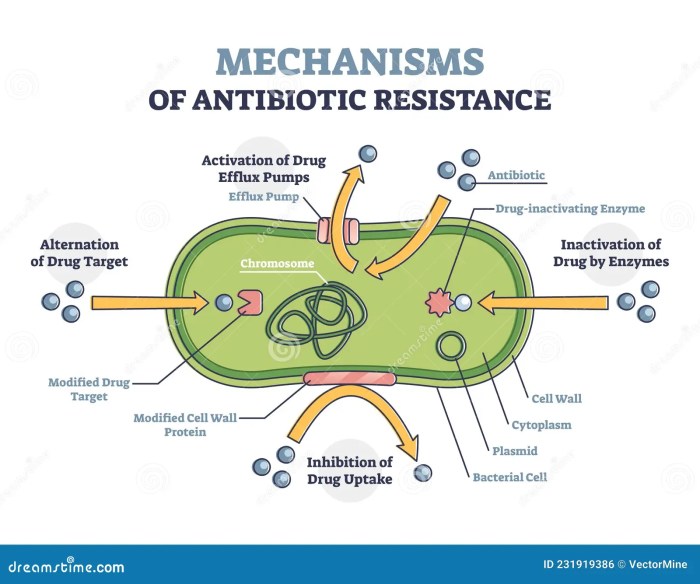
Antibiotic resistance arises from several factors, primarily the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. When antibiotics are prescribed inappropriately or used without proper adherence to the prescribed dosage and duration, bacteria have a higher chance of surviving and developing resistance.
Overuse and Misuse of Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed for viral infections, against which they are ineffective. Additionally, patients may fail to complete the prescribed course of antibiotics, leading to the survival of resistant bacteria. Self-medication with antibiotics without medical supervision further contributes to the problem.
Evolution and Development of Bacterial Resistance
Bacteria can evolve resistance through natural selection. When exposed to antibiotics, some bacteria possess genetic variations that confer resistance to the drug. These bacteria survive and reproduce, passing on their resistant genes to their offspring. Over time, the population of resistant bacteria increases, rendering the antibiotic ineffective.
Common Antibiotics and Their Effectiveness
- Penicillin:Effective against Gram-positive bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniaeand Staphylococcus aureus.
- Cephalosporins:Broad-spectrum antibiotics effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Escherichia coliand Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Fluoroquinolones:Used to treat respiratory and urinary tract infections caused by bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosaand Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Macrolides:Effective against Gram-positive bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniaeand Staphylococcus aureus.
- Tetracyclines:Broad-spectrum antibiotics used to treat infections caused by bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniaeand Chlamydia trachomatis.
Consequences of Antibiotic Resistance
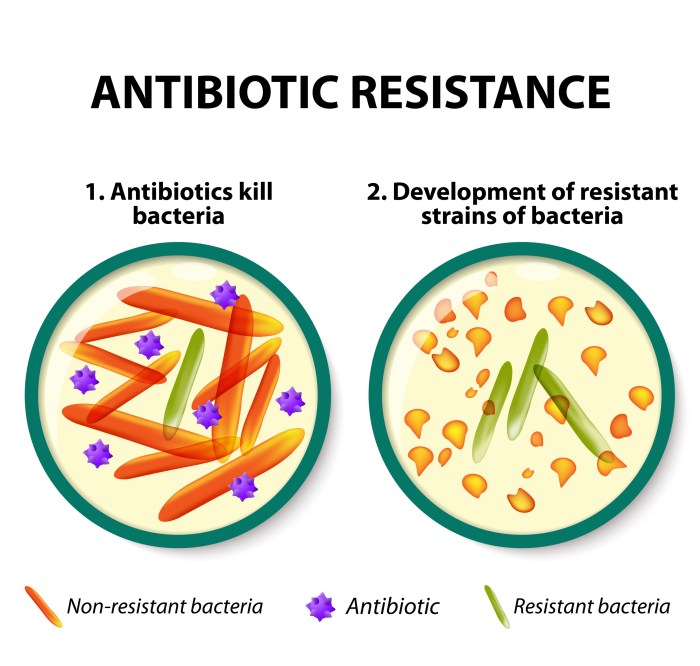
The consequences of antibiotic resistance are severe and far-reaching. Antibiotic resistance poses a significant threat to global public health, as it undermines the effectiveness of antibiotics, which are essential for treating bacterial infections.
Impact on Human Health
Antibiotic resistance has a profound impact on human health, leading to:
- Increased risk of severe infections and complications
- Longer hospital stays
- Higher healthcare costs
- Increased mortality rates
Examples of Resistant Infections
Examples of infections that are becoming increasingly difficult to treat due to antibiotic resistance include:
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA)
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus(VRE)
- Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae(CRE)
Post-Antibiotic Era
The potential for antibiotic resistance to lead to a post-antibiotic era, where common infections can no longer be treated with antibiotics, is a serious concern. This could result in a return to the pre-antibiotic era, where even minor infections could be fatal.
Prevention and Control of Antibiotic Resistance

Addressing antibiotic resistance requires a multifaceted approach that includes promoting responsible antibiotic use, implementing effective infection control measures, and investing in research and development efforts.
Responsible Antibiotic Use
- Antibiotics should only be prescribed when necessary, following appropriate diagnostic testing.
- Patients should adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment, even if symptoms improve.
- Leftover antibiotics should not be saved or shared, as they may promote resistance.
Infection Control Measures, Antibiotic resistance brain pop video
Preventing the spread of resistant bacteria is crucial in healthcare settings and the community.
- Hand hygiene, proper disinfection of surfaces, and appropriate use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are essential.
- Surveillance systems monitor antibiotic resistance patterns and identify outbreaks early on.
- Vaccination programs can prevent infections that may require antibiotic treatment.
Research and Development
Continued research is vital to combat antibiotic resistance.
- Developing new antibiotics with novel mechanisms of action is a priority.
- Exploring alternative therapies, such as bacteriophages or antimicrobial peptides, holds promise.
- Understanding the molecular basis of resistance can guide the development of effective interventions.
Antibiotic Stewardship
Antibiotic stewardship is a comprehensive approach to promoting the responsible use of antibiotics and preventing the emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance.
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in antibiotic stewardship by:
- Prescribing antibiotics only when necessary and at the appropriate dose and duration.
- Educating patients about the importance of taking antibiotics as directed and completing the full course of treatment.
- Monitoring for antibiotic resistance and implementing infection control measures to prevent its spread.
Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
Antibiotic stewardship programs are designed to improve antibiotic use and reduce resistance. These programs typically include:
- Guidelines for antibiotic prescribing.
- Antibiotic use surveillance and monitoring.
- Education and training for healthcare professionals and patients.
Studies have shown that antibiotic stewardship programs can significantly reduce antibiotic use and resistance. For example, a study in the United States found that a stewardship program reduced antibiotic use by 30% and antibiotic resistance by 15%.
Patient Education
Patient education is crucial in the fight against antibiotic resistance. Patients play a significant role in the responsible use of antibiotics, which can help reduce the development and spread of resistant bacteria.
Patients can contribute to responsible antibiotic use by understanding the following:
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Do not self-medicate with antibiotics or share them with others.
- Seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen after completing a course of antibiotics.
Proper Use of Antibiotics
- Take antibiotics exactly as prescribed, including the correct dosage, frequency, and duration.
- Do not skip doses or stop taking antibiotics early, even if symptoms improve.
- Store antibiotics properly according to the instructions on the label.
Conclusion

Antibiotic resistance is a global health threat that requires urgent action. By understanding the causes and consequences of antibiotic resistance, we can take steps to prevent and control its spread. Responsible antibiotic use, infection control measures, and ongoing research and development are crucial to preserving the effectiveness of antibiotics for future generations.
Ongoing Research and Development
The development of new antibiotics and alternative treatments is essential to combat antibiotic resistance. Researchers are exploring various approaches, including:
- Developing new antibiotics with novel mechanisms of action
- Modifying existing antibiotics to overcome resistance
- Investigating alternative treatments, such as bacteriophages and monoclonal antibodies
Continued investment in research and development is vital to ensure we stay ahead of the threat of antibiotic resistance.
FAQ: Antibiotic Resistance Brain Pop Video
What is antibiotic resistance?
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop mechanisms to evade the effects of antibiotics, rendering these drugs ineffective in treating infections.
How does antibiotic resistance develop?
Antibiotic resistance can develop through various mechanisms, including genetic mutations, horizontal gene transfer, and the formation of biofilms.
What are the consequences of antibiotic resistance?
Antibiotic resistance can lead to prolonged and severe infections, increased healthcare costs, and even death.
How can we prevent antibiotic resistance?
Responsible antibiotic use, infection control measures, and ongoing research and development are crucial in preventing and combating antibiotic resistance.